Amazon S3 Storage Classes: Hands-On | A Step-by-Step Guide
A step-by-step instructions on Managing Storage Classes in Amazon S3
Step 1: Navigate to Amazon S3 console
Open your web browser and go to the AWS Management Console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/.
Sign in to your AWS account using your credentials.
Once logged in, locate and click on "S3" under the "Storage" category. This will open the Amazon S3 console.
Step 2: Create a New S3 Bucket
You can follow the steps outlined in the "AWS S3 Console Hands-On | A Step-by-Step Guide" tutorial available at: S3 Console Hands-On | A Step-by-Step Guide
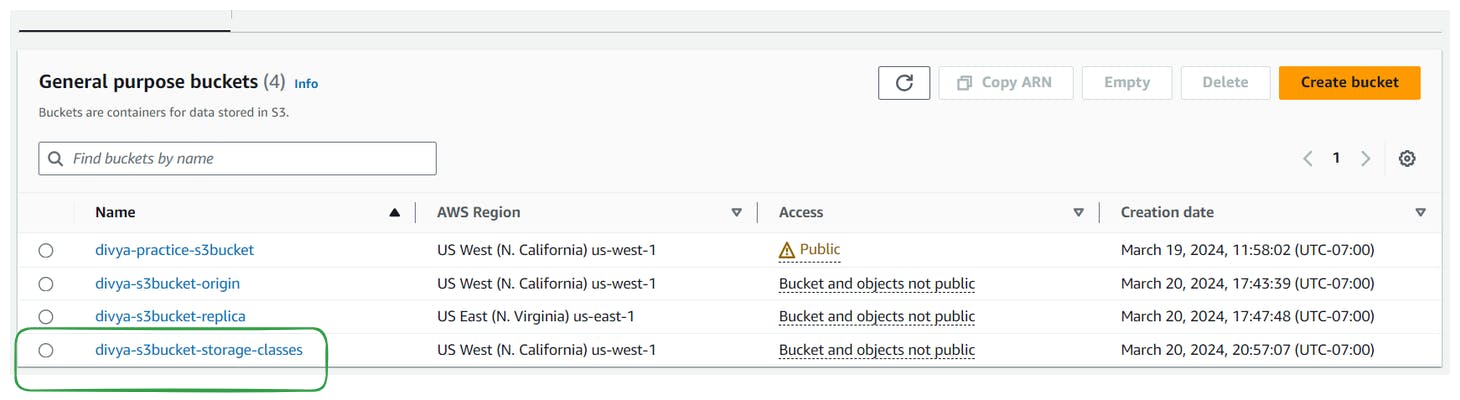
Go to the Amazon S3 console and create a new bucket with a suitable name, such as "divya-s3bucket-storage-classes"
Choose any desired region for the bucket and proceed with creating it.
Step 3: Upload Object and Set Storage Class
Upload an object (e.g., mountain.jpeg) to the newly created bucket.
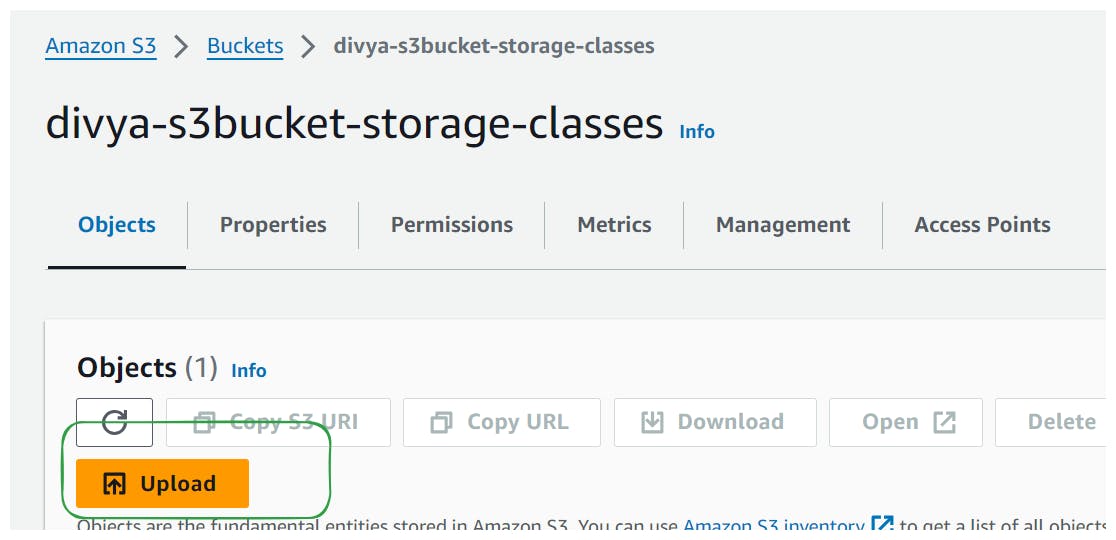
Click on the uploaded object and navigate to its properties.
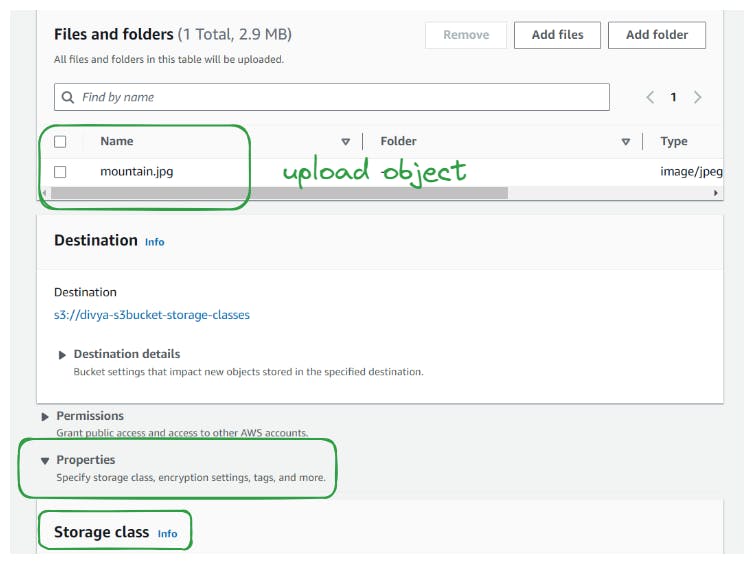
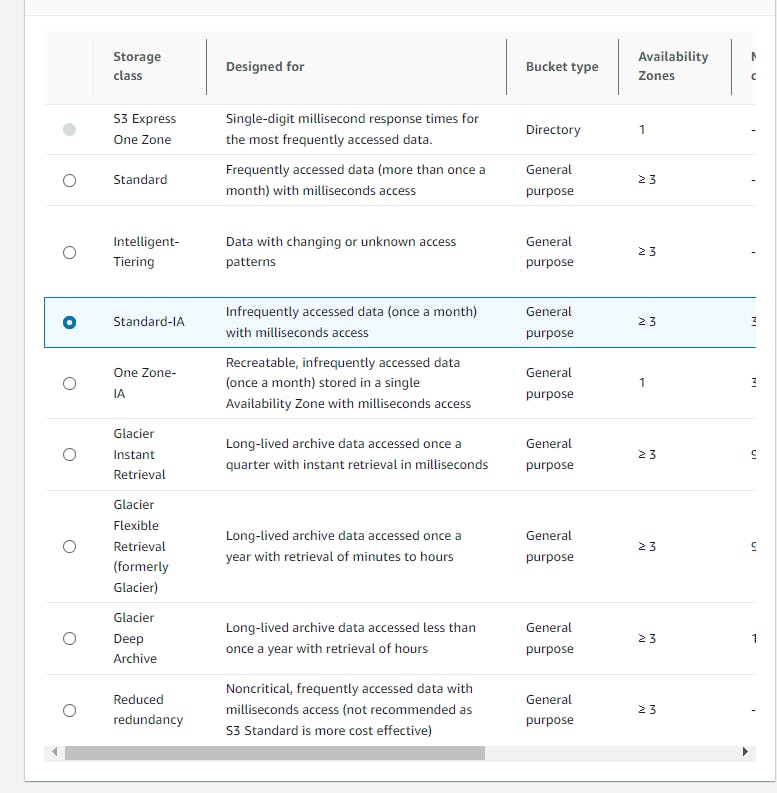
Under the "Storage Class" section, explore the available storage classes, including S3 Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, S3 Standard-IA, One-Zone-IA, Glacier options, and Reduced Redundancy.
Choose an appropriate storage class based on your requirements (e.g., S3 Standard-IA) and apply it to the object.
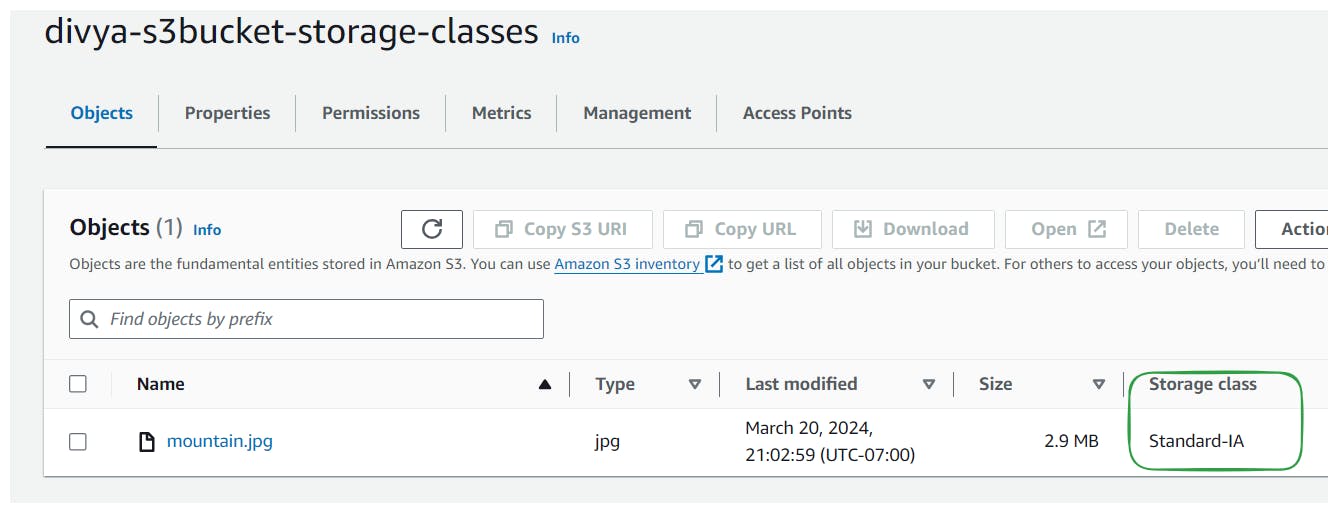
The class is visible in the Bucket along with the object details
Step 4: Change Storage Class (Optional)
Optionally, modify the storage class of the object by editing its properties.
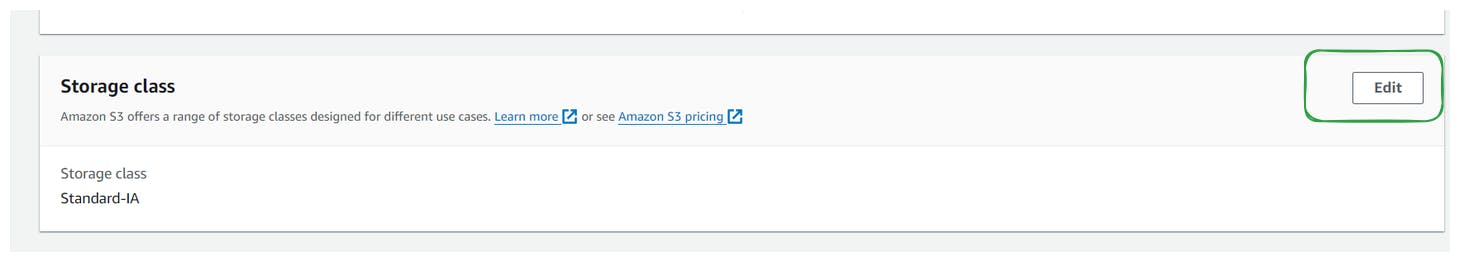
Select a different storage class (e.g., One-Zone-IA, Glacier options, or Intelligent-Tiering) and save the changes.
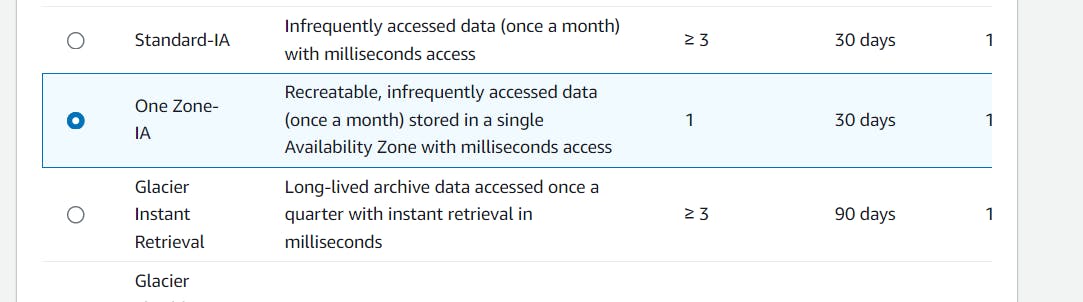
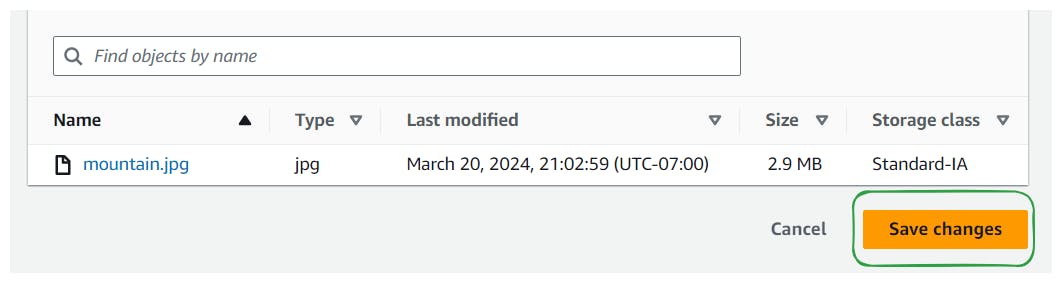
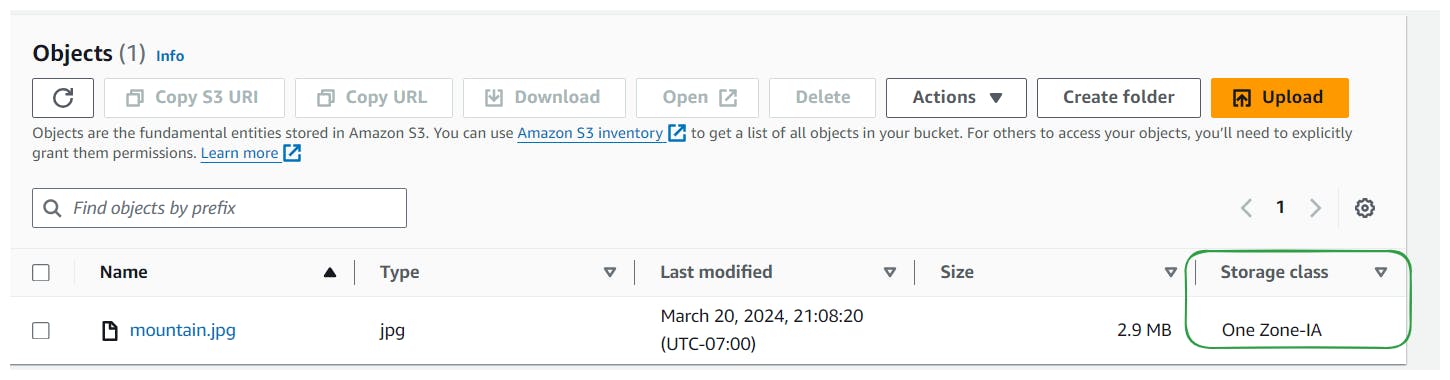
Verify that the storage class of the object has been successfully updated.
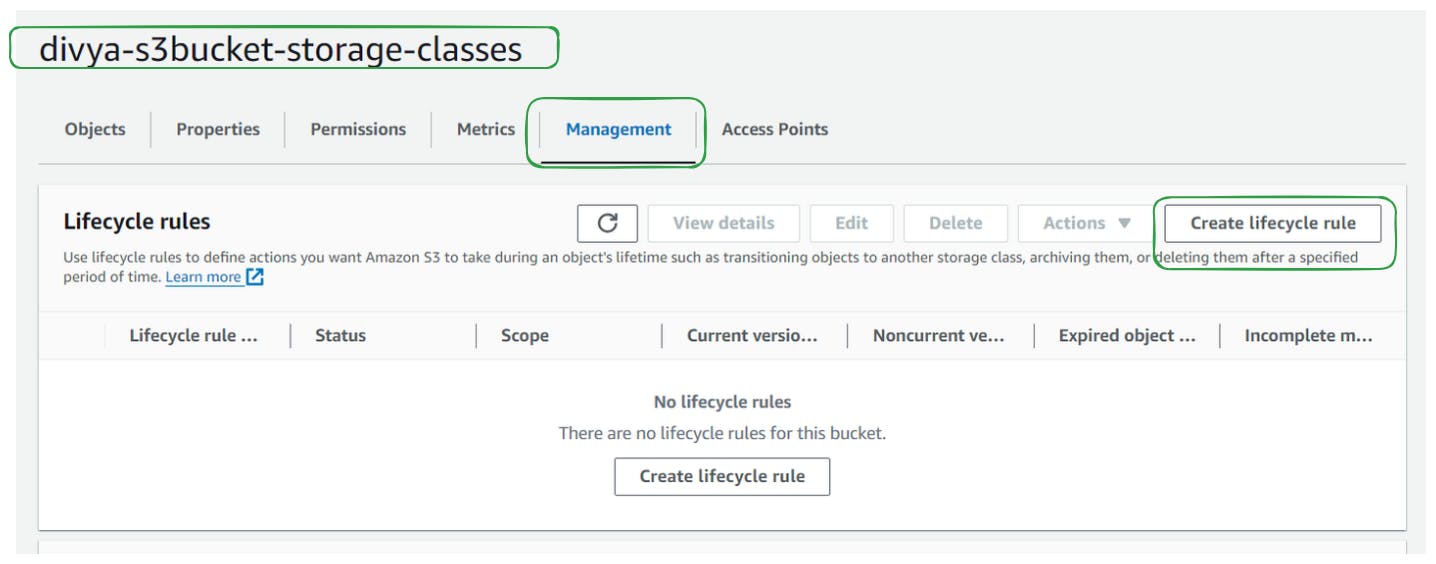
Step 5: Automate Storage Class Transitions with Lifecycle Rules
Navigate to the management section of the bucket and create a new lifecycle rule
Specify the rule to apply to all objects in the bucket.
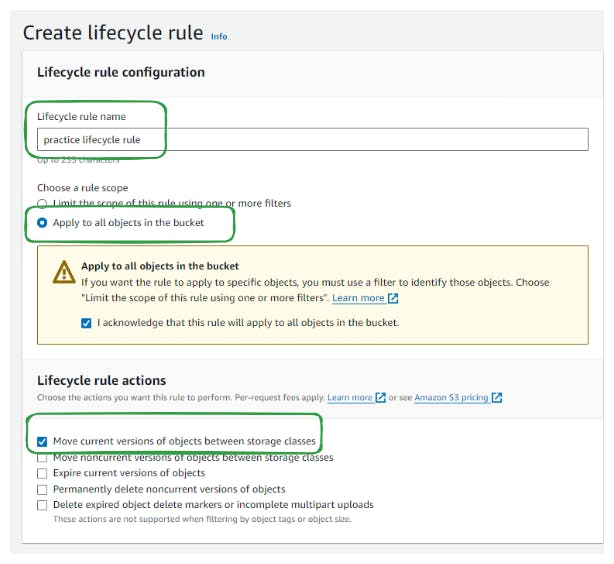
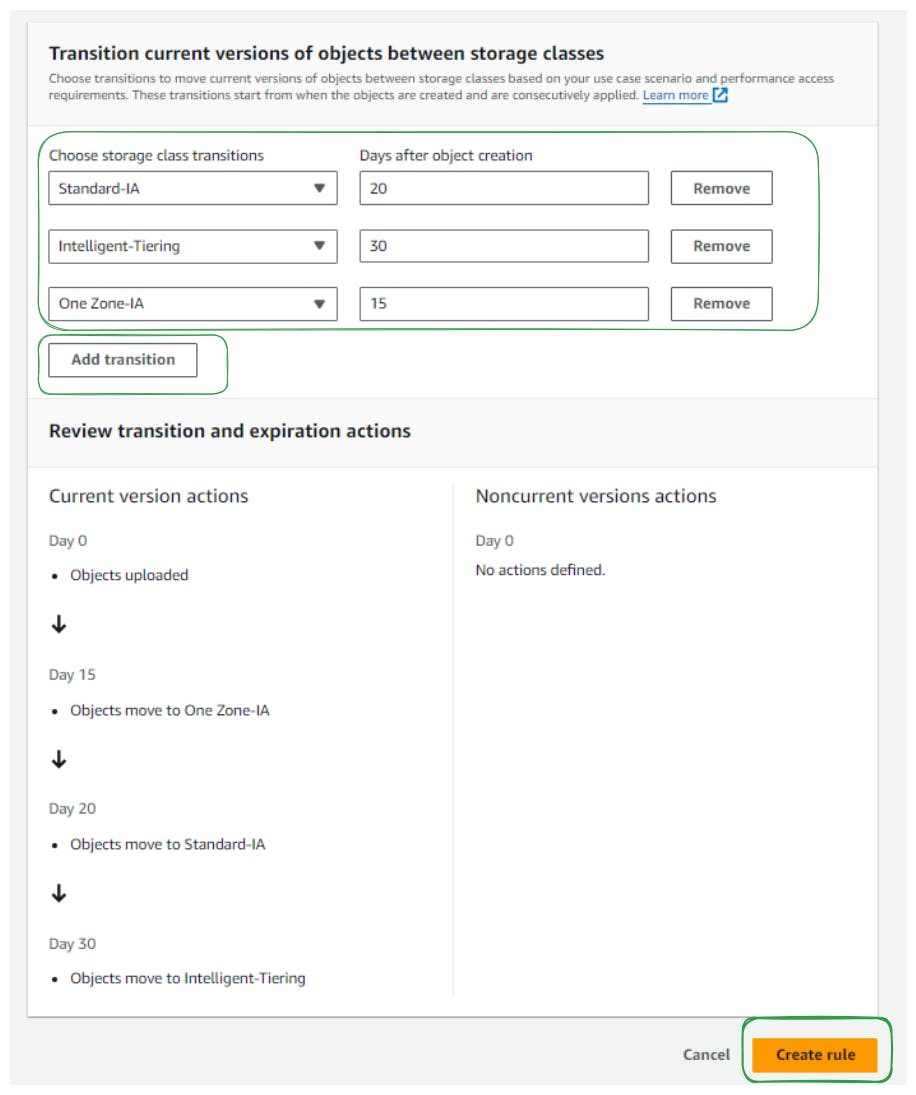
Define transitions between storage classes based on time intervals (e.g., move to Standard-IA after 30 days, Intelligent-Tiering after 60 days, Glacier-Flexible-Retrieval after 180 days, etc.).
Review and confirm the lifecycle rule settings to automate the movement of objects between storage classes.
Conclusion
Storage classes in Amazon S3 offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness by providing different options for storing data based on access patterns and requirements.
Utilize the appropriate storage class for your data to optimize performance, durability, and cost.
Automate storage class transitions using lifecycle rules to efficiently manage object lifecycle and reduce storage costs over time.
