A Beginner's Guide to Cloud Computing
Day1 : Prep- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner | CLF-C02
Link to exam: https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-cloud-practitioner/
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services—such as storage, processing power, databases, networking, and software—over the internet.
- Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware and infrastructure, users can access and utilize these services remotely through third-party cloud providers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The Five Characteristics of cloud computing
| Aspect | Description | Example |
| On-demand self-service | Provision computing resources without human interaction from the service provider. | Provisioning virtual machines (VMs) for application testing. |
| Broad network access | Access cloud resources over the internet from any device. | Accessing CRM software from laptops, tablets, or smartphones. |
| Resource pooling and multi-tenancy | Share and allocate resources among multiple users securely without monopolizing entire resources | Hosting multiple virtual servers from different organizations on the same physical hardware. |
| Rapid elasticity and scalability | Scale resources up or down quickly to adapt to workload changes, optimizing cost. | Automatically increasing server capacity during peak shopping seasons for an e-commerce site. |
| Measured service | Pay for actual resource usage, ensuring cost-effectiveness. | Paying for the data transferred by a video streaming service. |
Deployment Models
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Ownership | Third-party providers | Organization-owned | Combination |
| AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform | Company XYZ's private data center | Company ABC using AWS for some services and private servers for others | |
| Accessibility | Over the internet | Within company's network | Both |
| Infrastructure Control | Limited | Full | Varied |
| Security | Provider-managed | Organization-managed | Combination |
| Customization | Limited | Full | Varied |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Depends on infrastructure | Varies based on deployment model |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go | Initial investment + operational costs | Varies based on deployment model |
| Compliance | Provider certifications | Organization control | Varied |
Service Models
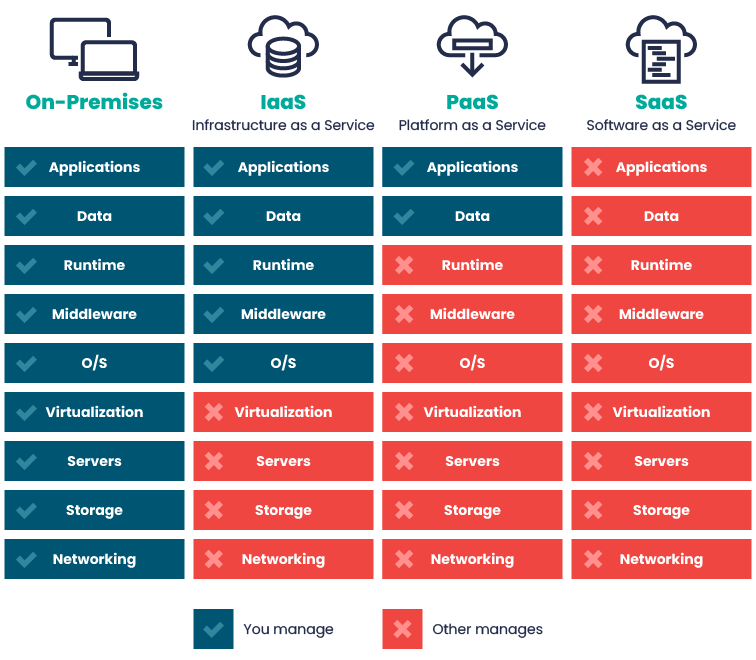
Reference: https://www.nearshore-it.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/nearshore_2023.07.17_graphic_1.png
| Aspect | On-Premise | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Scalability | Limited | High | Platform-dependent | High |
| Flexibility | Limited | Flexible | Moderate | Limited |
| Control | Full | Less | Limited | Minimal |
| Maintenance | User | Provider | Provider | Provider |
| Examples | In-house data centers, self-hosted software. | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform. | Heroku, Google App Engine, Azure App Service. | Salesforce, Google Workspace, Dropbox. |
The Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
| Advantage | Description | Example |
| Trade fixed expense CAPEX for variable expense OPEX | Pay only for the computing resources you use, avoiding upfront investments in data centers and servers. | Paying for storage and processing power used. |
| Lower costs | Access lower costs by leveraging cloud provider's aggregated usage, resulting in reduced pay-as-you-go prices. | Achieving lower infrastructure costs. |
| Stop guessing capacity | Scale resources up or down as required, eliminating the need for forecasting infrastructure needs and dealing with over-provisioning or under-provisioning. | Scaling up server capacity during peak traffic. |
| Increase speed and agility | Provision new IT resources rapidly, accelerating experimentation, development, and deployment processes. | Launching new application features quickly. |
| Reduced TCO and OPEX by avoiding running and maintaining data centers | Shift focus from managing infrastructure to delivering value to customers, freeing resources for innovation and business growth. | Investing in customer-centric applications. |
| Go global in minutes | Deploy applications globally with minimal effort, providing low-latency access and a superior user experience worldwide. | Launching web applications internationally. |
Reference:docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-..
Problems Solved by cloud computing
| Problem | Solution |
| Flexibility | Scale resources as needed for changing demands. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Pay only for resources used, reducing upfront costs. |
| Scalability | Scale resources up or down to handle varying workloads. |
| Elasticity | Dynamically on demand, allocate resources in real-time. |
| High availability | Redundant infrastructure and data replication across multiple locations ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime. |
| Fault tolerance | Maintain reliability against hardware failures + disruptions |
| Agility | Rapidly develop and deploy applications. |
| Data security and compliance | Protect data with robust security measures + certifications |
| Collaboration and remote work | Facilitate teamwork and remote work. |
